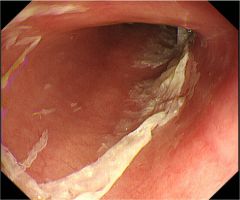
(BMJ)—A 68-yo man treated w/ dabigatran for recently diagnosed afib had his annual upper GI endoscopy. It revealed sloughing mucosal casts and mild esophageal erythema that were not previously present. Bx: esophageal mucosa w/o dysplasia. What is the dx?
|
Pemphigoid-related esophagitis
|
|
Ischemic esophagitis
|
|
Eosinophilic esophagitis
|
|
Dabigatran-induced exfoliative esophagitis
|
|
Candida esophagitis
|
